Adrien Ruggiero

Artificial intelligence and data science enthusiasts, my ambition is to become a data scientist. I love to get involved in data science projects on projects that interest me.
View my LinkedIn profile
Object Tracking with the Kalman Filter
1. About this project
This project tackled traditional object detection using the well known Kalman Filter. The Kalman filter is an algorithm that will try to predict the estimates of various variables from noisy input data. It will thus allow to determine the state of a dynamic system. The code is available here.
This project was done in a school context with another classmate. The idea was to become familiar with computer vision and image processing, the scope and the subject were free.
2. The principle of this filter
This filter was developed by Rudolf Emil Kalman in the 60s. As mentioned in the introduction, it is an algorithm that will try to predict the state of a moving system.

It is an iterative process that takes into account the incertia and variations associated with the input data. This filter is split in two parts :
- The prediction
- The correction
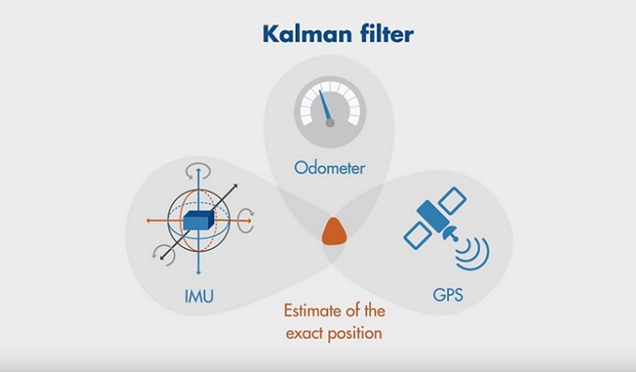
This filter is used in many fields such as geolocation or medical with image reconstruction. We can of course apply this filter in a one-dimensional case and in a multi-dimensional case by extending the operations and the variables to a matrix representation.
There are three important steps:
- The calculation of the gain.
- The calculation of the estimate
- The calculation of the estimation error
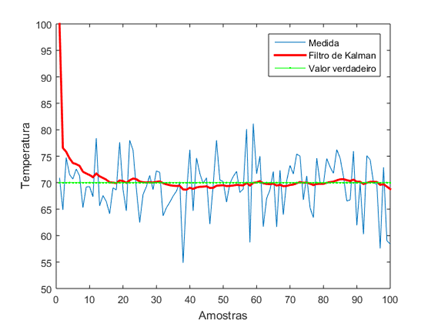
It is the gain (KG) that determines whether one gives weight to the estimates or to the data. It will also dicate how quickly the estimated value converges (or not) to the true value.
As the gain decreases and gets closer to 0, the estimated value gets closer and closer to the true value. On the contrary, if KG is close to 1, it means that the measurements are accurate, contrary to the values estimated during the iterations which are rather unstable.
The difference between the case in 1D and in higher dimensions is that for the higher dimensions we will add a perturbation matrix to allow the system to continue to evolve and converge.
We also use the covariance to represent the error in the estimation or in the process.
To have more details on the relations and mathematical principles, I invite you to download and watch the presentation slideshow.
In our examples, we use the Euclidean distance to evaluate the distance separating objects from an upcoming state. Also, to facilitate the use of the Kalman filter, it is interesting to proceed to a pre-processing. Hence the calculation of the mask and the median for our bees.
3. The videos
In my case, I am looking to apply the filter on two examples:
- People walking down the street
- Bees flying near a surface
I had a video of bees available, so I used it as a secondary example to see if I could apply the filter correctly to a “lambda” video as well.
Concerning the perosnnes, we used an open source database directly extracted from the website Multiple Object Tracking Challenge where we can find videos with many configurations:
- Fixed or mobile camera
- High population or not
- Overlay or not
- High illumination or not

When you download a video, you get a succession of images that will constitute the video during playback. Also, we have an associated text file which for each image will have information on the people in particular their position to be able to identify them.

Here, we have 8 persons that can be identified at frame n°584
Indeed, the Kalman filter is used to predict a state not to recognize an object or a person. It is therefore necessary to couple this algorithm with another script that will allow to locate and identify the events of interest.
## 4. The advantages and disadvantages of the Kalman filter.
First of all concerning the negative points :
- Stability and therefore convergency are not guaranteed for non linear systems
- It is necessary to assume a probability of presence and a certain Gaussian noise
- The reaction time is high in case of abrupt state change
- A very detailed and known modeling of the problem is required (especially when assigning and distributing forces, accelerations and other parameters for our matrices)
Then, this filter still has many advantages such as:
- An estimation from noisy data for a dynamic system
- It is multi-domain
- Its prediction capacity
- Its capacity of error correction
- It can be applied to linear AND non-linear systems
- Certainty of convergence in the linear case